What Is Database Scalability? Strategies for Scaling Your Database
Database scaling refers to the method of increasing a database system’s capacity to handle workload growth caused by higher query volumes, increased transaction rates, or expanding datasets, without degrading performance.
What Does Database Scalability Mean?
Database scalability refers to how well a database can accommodate growth, whether by leveraging more powerful hardware or by distributing the load across additional machines.
In practical terms, a highly scalable database is one that can grow (or shrink) rapidly, with predictable cost and minimal administrative overhead, as business requirements evolve.
In the context of cloud-native environments, robust database scalability is essential for supporting dynamic, business-critical applications that require elasticity, resilience, and reliability.
Why Is Database Scalability Important for Modern Databases?
The importance of database scalability cannot be overstated. Businesses that rely on modern, cloud-native applications must be able to meet unpredictable spikes in demand, seasonal traffic fluctuations, or global expansion.
A database that doesn’t easily scale quickly becomes the bottleneck that stifles innovation, impacts customer experience, and jeopardizes revenue.
Effortless scalability enables organizations to unlock new markets, deliver uninterrupted customer experiences, and recover rapidly from hardware or network failures.
Distributed SQL databases like YugabyteDB are purpose-built to meet these evolving demands by unifying strong consistency, automated failover, and seamless elasticity. When your existing database server begins showing performance latency it’s often time to evaluate your database infrastructure for scaling.
What Are the Best Strategies for Scaling Databases?
Core database scaling strategies include vertical scaling (scale‑up) and horizontal scaling (scale‑out), but advanced approaches include sharding, data partitioning, caching, and distributed SQL.
Each method presents unique trade-offs and operational considerations, especially as demands shift toward geo-distribution and cloud-native resilience.
Below, we explore some of the differences between these strategies.
What Is the Difference Between Scaling up (Vertical) and Scaling Out (Horizontal)?
Vertical Scaling
Scaling up (vertical scaling) involves upgrading the compute, memory, or storage capacity of a single database server. In practice, this might involve upgrading from a 4-core server to a 32-core machine, increasing RAM, or installing faster SSD storage.
Legacy SQL RDBMS often require vertical scaling to accommodate increased loads. While initially simple to implement, vertical scaling has fundamental limitations. As demand surpasses the capacity of even the largest servers, organizations may encounter significant costs and operational complexities.
Vertical scaling generally:
- Requires downtime during hardware upgrades or migrations
- Introduces vendor lock-in to specialized hardware
- Dramatically increases operational costs due to the need for high-performance components
Horizontal Scaling
In contrast, scaling out (also known as horizontal scaling) is the process of adding more servers or nodes (typically commodity hardware) to a database cluster.
Rather than grow the capabilities of a single machine, applications and data are distributed across multiple nodes that work in tandem, enabling virtually unlimited growth and improved resiliency.
Adding or removing nodes is accomplished with minimal (or zero) downtime, as the system automatically rebalances data and workload across the expanded cluster. This approach enables near-infinite scalability, allows IT teams to respond dynamically to changing business demands, and avoids the cost and operational complexity associated with large, monolithic servers.
Horizontal scaling is a foundational trait of cloud-native databases and distributed SQL.
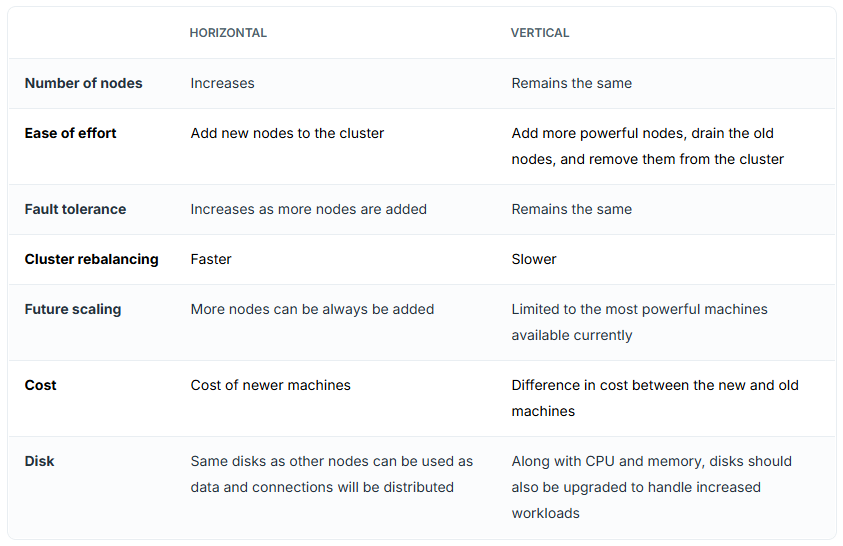
Because YugabyteDB is distributed, scaling is operationally straightforward and performed without any service disruption, regardless of the scaling method you choose. This table lists the pros and cons of horizontally or vertically scaling a YugabyteDB cluster.
What is the Difference Between Sharding and Partitioning Data?
To scale beyond a single-node database, sharding (splitting data across independent database instances) is often required. Manual sharding introduces complexity into the application layer, making resharding and managing hotspots operationally challenging.
In contrast, YugabyteDB implements automatic sharding within its architecture, partitioning each table into tablets and distributing them across available nodes. This self-managing approach allows applications to scale without code changes and with strong consistency guarantees.
Read Replicas and Caching for Workload Optimization
Read replicas distribute read traffic across multiple database nodes, relieving write-intensive primaries and improving latency. Caching, both at the database and application layer, further optimizes workload by storing frequently accessed data in memory.
These approaches introduce potential consistency issues and require careful orchestration with transactional workloads. Distributed SQL solutions streamline replication and offer tunable consistency levels to balance performance and correctness for different use cases.
How Does Distributed SQL Provide Seamless Scale and Strong Consistency?
Distributed SQL combines the feature set of traditional RDBMS (relational APIs, ACID transactions, and SQL compatibility) with the scale-out benefits of NoSQL.
As a leader in this space, YugabyteDB delivers seamless scaling with strong consistency through advanced consensus protocols (e.g., Raft), automated balancing, and transparent failover.
Applications benefit from high availability, automatic data distribution, and the flexibility to elastically add or remove compute resources on demand, all without sacrificing SQL support or transactional guarantees. Relational databases scalable across distributed clusters bridge the gap between traditional SQL databases and modern cloud demands.
What Is Geo-Distribution for Global Applications and Disaster Recovery?
For organizations with globally distributed users or strict disaster recovery targets, geo-distribution is essential. This involves deploying database nodes and data shards across multiple regions.
YugabyteDB provides multiple geo-distribution options (including synchronous and asynchronous replication, and row-level geo-partitioning) to serve users close to their data, meet data residency requirements, and ensure business continuity.
Unlike legacy databases, configuration is simplified and automatic, enabling modern applications to meet today’s lowest latency and highest availability demands.
Scaling Down for Cost Efficiency
Elasticity isn’t just about scaling up for growth; scaling down during off-peak periods is critical for controlling costs in cloud environments.
Distributed SQL databases inherently support scale-in by allowing operators to deprovision nodes as workload declines, without risk of data loss or application impact. This enables IT teams to align their infrastructure spend with actual business demand, a key advantage over legacy or statically-partitioned environments. Maintaining system performance while scaling down is just as important as scaling up.
How Do Relational and Distributed SQL Databases Maintain Consistency Under Load?
Modern relational databases such as PostgreSQL and cloud-native, distributed systems provide robust, parallelized concurrency control, ensuring strong consistency (no dirty or stale reads) across thousands of simultaneous connections.
Distributed SQL databases take it further by ensuring ACID guarantees and isolating user transactions across geo-distributed nodes, maintaining correctness regardless of node, zone, or region failures. When distributing data across multiple servers, database architects must ensure that the same data is synchronized and available to avoid divergence.
How Do You Compare Automatic to Manual Scaling Processes?
The distinction between automatic and manual scaling processes is especially important for modern, always-on applications.
Traditional databases require manual intervention for hardware upgrades and often involve scheduled downtime, significant pre-planning, and complicated migrations. In contrast, distributed SQL databases like YugabyteDB offer auto-sharding, where data is automatically partitioned and rebalanced when new nodes join the cluster.
Integration with cloud orchestration tools enables auto-scaling, where resource allocation matches real-time workload demands, crucial for cloud-native and microservices-based architectures. This leads to operational simplicity and cost efficiency, as infrastructure is right-sized at every moment. Choosing scalable database architectures early helps avoid bottlenecks when data volumes explode.
Operational Considerations: Downtime, Complexity, and Cost
IT professionals must balance three key considerations when scaling their databases.
- Downtime: Vertical scaling is often limited by the capacity of a single server, resulting in service interruptions, which can impact application availability. Horizontal scaling involves adding multiple servers or nodes to distribute the load, enabling you to scale without downtime and enhance system resilience and availability.
- Complexity: Manual sharding and scaling logic in the application layer is prone to errors and burdensome to maintain. Distributed SQL automates sharding, replica management, and failover, simplifying operations and reducing the risk of human error.
- Cost: Specialized hardware for vertical scaling is expensive, leading to over-provisioning. Horizontal scaling leverages commodity hardware, spreading cost across many smaller instances and supporting true pay-as-you-grow economics. Automated scaling can also reduce unnecessary resource spend during periods of reduced demand. A scalable database architecture must address database load, distributed transactions, and the trade‑offs between performance, consistency, and cost.
Scaling a database effectively means leveraging modern distributed SQL capabilities to achieve operational agility, cost efficiency, and business continuity. Databases like YugabyteDB reduce the operational burden, enabling IT professionals and database architects to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure maintenance. A robust database architecture enables your system’s growing data storage needs to be met without compromising on data availability or query responsiveness.
What Are Some Scalable Database Examples and Modern Approaches?
When evaluating scalable database examples for modern application demands, IT professionals and database architects have more options than ever, thanks to the emergence of distributed SQL and cloud-native architectures.
Databases like YugabyteDB bring true horizontal scalability, availability, and strong consistency across distributed environments. Unlike legacy RDBMS or basic NoSQL solutions, these databases natively solve the challenges posed by high transaction volumes, global distribution, and dynamic, elastic workloads.
PostgreSQL-Compatible Distributed SQL Databases
One of the most impactful trends in cloud-native databases is deep PostgreSQL compatibility. Some databases offer PostgreSQL wire protocol and syntax support, allowing developers to leverage familiar tools, drivers, and frameworks. However, YugabyteDB achieves full runtime compatibility, extending feature coverage well beyond the basics by supporting stored procedures, rich indexing, triggers, and advanced extensions. This makes it possible to migrate mission-critical workloads to a distributed SQL database with minimal code changes. Check out open source migration tool, YugabyteDB Voyager, for details on how you can transition from PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, and cloud databases to YugabyteDB. When modernizing from traditional SQL databases toward scalable database architectures, the path often involves hybrid models, replication, and partitioning.
Comparing Distributed SQL to Traditional RDBMS and NoSQL
Traditional RDBMS like Oracle, SQL Server, and vanilla PostgreSQL offer robust relational capabilities, but often struggle with horizontal scalability, high availability, and cloud-native automation. NoSQL databases deliver excellent horizontal scaling but lack robust SQL semantics and ACID guarantees, even as they push toward distributed transactional support.
Distributed SQL databases bridge these gaps, offering developers the best of both worlds: full relational model and syntax, transactional integrity, and elastic, global scalability.
This makes them the foundational data layer for next-generation applications (particularly in sectors like financial services, telco, and e-commerce, where data correctness, resilience, and scale are crucial). Relational databases scalable via sharding and replication can maintain the relational model while distributing data for high volume workloads.
Embracing Distributed SQL for Seamless Database Scalability
As enterprises increasingly depend on real-time, globally accessible applications, the need to scale beyond the limitations of monolithic databases is critical. Modern IT landscapes require scaling relational databases seamlessly (both horizontally and vertically) while ensuring operational simplicity, strong consistency, and the flexibility demanded by cloud-native agility.
Distributed SQL databases like YugabyteDB blend the familiarity of traditional relational databases with the benefits of distributed architectures.
By distributing data across multiple locations, these systems deliver high availability and durability while meeting stringent SLAs for uptime and performance. Features like built-in geo-distribution, tunable consistency, and automated sharding enable you to match infrastructure to workload, regardless of how unpredictable business growth and demand may be.
Distributed SQL is a class of cloud-native, highly scalable, and resilient databases designed for today’s always-on, data-driven world. Download the new Distributed SQL Databases For Dummies (2nd Yugabyte Special Edition) eBook and explore how distributed SQL can help you achieve ultra-resilience, simplify operations, accelerate innovation, and future-proof your next GenAI applications.
Contact us today, and unlock the potential of distributed SQL with YugabyteDB.