Distributed SQL 101
What is Distributed SQL?
Distributed SQL is a category of relational databases that combines the core features of traditional SQL and NoSQL systems, being strongly consistent while natively providing ACID transactional support across data centers, availability zones, and regions—in the cloud.
It provides a single logical relational database deployed across a cluster of network servers. Distributed SQL databases automatically replicate and distribute data among those servers, often called nodes, which can handle both read and write queries.
The nodes communicate with each other and form a network called a cluster, which can span across a data center or across the world in geographically distributed locations. Just add more nodes to scale. The database orchestrates how nodes in a cluster work together to store, balance, replicate, and retrieve data. When you query your tables, the database determines the best access path to your data, whether it’s close to your client or geographically distant.
Geo-Distribution and Engineering Around the Physics of Latency>>>
Is Distributed SQL a New Breed of Database?
Distributed SQL databases were introduced in the mid-2010s for transactional applications. They deliver core features found in both relational (SQL) or non-relational (NoSQL) databases. The database is horizontally scalable, strongly consistent, and natively provides ACID transactional support across availability and geographic zones in the cloud or in on-premises data centers.
Differences Between SQL and Distributed SQL
Unlike a monolithic SQL database, a distributed SQL database:
- Is resilient to failures, protecting critical data and applications
- Scales horizontally to easily support workload increases and decreases, and support business growth
- Supports a geo-distributed cluster topology spanning multiple regions and cloud providers to deliver an always-on, consistent experience to users anywhere in the world
- Provides a high level of SQL compatibility, with standard relational database management features and functionality
- Matches your database architecture with container and Kubernetes developer environments that improve business agility
- Improves data visibility and real-time data analysis to reduce security risk
 Click on infographic to learn more
Click on infographic to learn more
Architecture of Distributed SQL
Distributed SQL databases are rapidly gaining popularity among organizations seeking to modernize their data layer. This shift is often driven by a desire to better support geo-distributed, cloud-native applications, reduce total cost of ownership (TCO), and/or overcome the horizontal scaling limitations of monolithic RDBMS such as Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQL Server.
The fundamental architectural components of a distributed SQL database include:
- A robust SQL API for querying and modeling data, along with support for traditional RDBMS features like foreign keys, partial indexes, stored procedures, and triggers.
- Automatic and transparent distributed data storage that includes sharded indexes across multiple nodes in the cluster, avoiding a single node becoming a bottleneck. This ensures high performance the application and high availability of the data.
- Smart distributed query execution, which enables query processing to be executed closer to the data rather than pushing data over the network, leading to slower query response times.
- Support for strongly consistent replication and distributed ACID transactional support.
How Does Distributed SQL Work?
A distributed SQL database architecture is generally divided into two primary layers: the query layer and the storage layer.
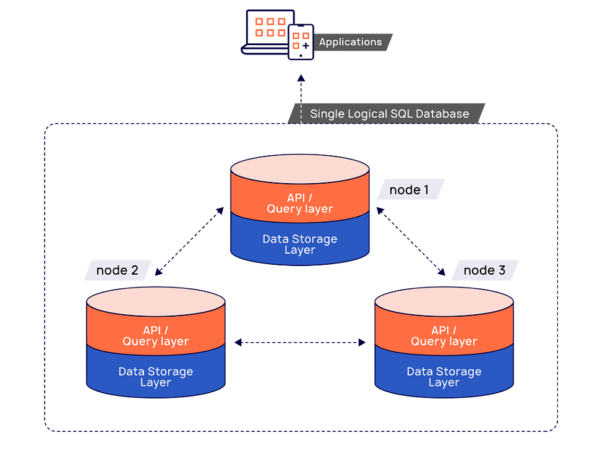
- API/Query Processing Layer. The API/query processing layer is responsible for language-specific query/command compilation, execution, and optimization. Applications interact directly with the query layer using client drivers.There is an SQL API in this layer for applications to model relational data and to perform queries involving those relations. Those queries are then automatically distributed across multiple nodes of the database cluster by the distributed data storage layer.
- Distributed Data Storage Layer. Data (including indexes) in a distributed SQL database are automatically distributed—or sharded—across multiple nodes of the cluster so that no single node becomes a bottleneck, ensuring high performance and availability.The underlying data storage layer supports the robust SQL API layer by automatically replicating data synchronously—across multiple nodes—to guarantee availability during failures, ensure transactional integrity, and maintain data consistency. No operator intervention is needed; it is done using the Raft distributed consensus protocol.Additionally, the database storage layer supports distributed ACID transactions, modifying multiple rows distributed across shards on multiple nodes for absolute data integrity and safety.Learn more about the two-layer architecture of a distributed SQL database
Benefits of Distributed SQL
A distributed SQL database combines the best features of traditional RDBMSs with the innovation of cloud native databases to:
- Accelerate developer productivity by building new features and services quickly
- Unlock the potential of your apps by scaling with them up, or down, as needed
- Improve your customer experience by exceeding uptime SLAs
- Reduce operational costs with lower TCO by only paying for what you need
- Protect your critical data in production environments with built-in security controls
- Seamlessly upgrade from your legacy database with advanced migration tools
Why Are Distributed SQL Databases Needed?
For decades the relational database has, by default, served as the system of record for mission-critical applications. But non-distributed, monolithic SQL databases like Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, EDB PostgreSQL, and IBM DB2 run on a single server. This means that they can only scale up to the maximum amount of CPU, memory, disk, and network bandwidth that the one server can offer.
With an increasing percentage of transactions coming from an exponentially growing set of cloud-based, connected applications, workloads increase dramatically.
As a result, stand-alone, traditional SQL databases quickly run out of resources. At this point, the best-case scenario is that latency skyrockets, and these new application connections and transactions wait in a long queue. The worst -case scenario is that the database crashes, bringing business transactions to a halt.
Monolithic databases constitute a significant risk for cloud native applications which require an always-available database that can scale as transactions grow or contract as demand shrinks.
How Distributed SQL Supports Database Modernization Initiatives and Cloud Native Applications
The need to innovate and grow is forcing companies to deliver born-in-the-cloud applications (in the form of microservices) and embrace edge computing frameworks and streaming workloads. The requirement to support diverse workloads, along with the drive to lower IT costs and reduce risk through better compliance, puts pressure on traditional, monolithic systems of record databases.
To fully benefit from the advantages of modern, cloud native applications, frameworks, and workloads, your IT stack must incorporate a new class of database. This should bring a core set of capabilities that align with your application and infrastructure transformation initiatives:
- Resilient to failures and continuously available. Fast failover capabilities mean that critical services remain available during node, zone, region, and data center failures, as well as during regular system maintenance.
- Horizontally scalable. To handle more transactions per second or a higher number of concurrent client connections or larger datasets, a distributed SQL database can be effortlessly scaled out—even under heavy load—without downtime simply by adding nodes to a running cluster. It can be scaled back just as easily when the load decreases.
- Geographically distributed. To distribute data globally and control precisely where the data lives, distributed SQL uses synchronous and asynchronous data replication and geo-partitioning to deploy the database in various geo-distributed configurations. Distributed SQL databases support the building of geo-distributed applications, helping to overcome region failures automatically and lower latency for end users by bringing data closer to their local region.
- SQL and RDBMS feature compatibility. Your developers no longer need to choose between the horizontal scalability of cloud native systems and the ACID guarantees and strong consistency of a traditional RDBMS. A distributed SQL database supports ACID transactions without trading the resiliency (to failures) and scalability that mission-critical, cloud native systems demand.
- ACID transaction support. Distributed SQL databases are designed for systems of record. They supply transactional integrity and strong consistency from the ground up with coordinated writes, locked records, and other methods including multi-version concurrency control.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud ready. Organizations can deploy and run their data infrastructure anywhere to reduce costs, avoid vendor lock-in, and simplify processes.
The Need For a Distributed SQL Database
For decades the relational database has by default served as the system of record for mission-critical applications. But non-distributed, monolithic SQL databases like Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, EDB PostgreSQL, and IBM DB2, run on a single server. This means that they can only scale up to the maximum amount of CPU, memory, disk, and network bandwidth that the one server can offer.
With an increasing percentage of transactions coming from an exponentially growing set of cloud-based, connected applications, workloads increase dramatically.
As a result, stand-alone, traditional SQL database quickly run out of resources. At this point, the best-case scenario is that latency skyrockets and these new application connections and transactions wait in a long queue. The worst-case is that the database crashes, bringing business transactions to a halt.
Monolithic databases constitute a significant risk for cloud native applications which require an always-available database that can scale as transactions grow or contract as demand shrinks.
How to Get Started with Distributed SQL
Whether you’re a cloud native application developer, architect, or database operator, you would benefit from a database that can handle your most demanding workloads. Distributed SQL combines enterprise-grade, relational database capabilities with the horizontal scalability and resilience of cloud native architectures.
Get started with distributed SQL>>>
Why YugabyteDB Is the Only Distributed SQL Database You Need
YugabyteDB is the cloud native distributed SQL database for mission-critical applications. Companies using YugabyteDB for their scale-out RDBMS and internet-scale OLTP workloads benefit from a distributed database that is:
- PostgreSQL compatible. YugabyteDB reimagines PostgreSQL for a cloud native world. It reuses the PostgreSQL query layer and supports all advanced features, including triggers, stored procedures, user-defined functions, and expression indexes. This familiarity and compatibility reduces developer onboarding time and costs, allowing them to get productive quicker.
- Horizontally scalable. YugabyteDB is proven in production environments to scale beyond 3000K TPS, over 100 TB of data, and thousands of concurrent connections, allowing you to scale out and in with zero impact.
- Resilient to failures. Ensure continuous availability during infrastructure failures and maintenance tasks.
- Geo-distributed. Use replication and data geo-partitioning capabilities to achieve the latency, resiliency, and compliance your applications need.
- Secure. With key security features built into the data layer, including authentication, authorization, and encryption, you can ensure you build a safe business.
- Enables hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. The freedom to deploy in public, private, and hybrid cloud environments on VMs, containers, or bare metal.
Request a free trial of YugabyteDB>>>
Distributed SQL FAQ
- Can SQL databases be distributed?
Yes, a distributed SQL database’s architecture allows for quick and easy scalability to support fluctuating transactional workloads. They are horizontally scalable, strongly consistent, and offer ACID guarantees. - What are the benefits of distributed SQL?
Distributed SQL offers many benefits. It boosts developer productivity, scales to support app needs, is resilient and highly available, reduces operational costs, lowers TCO, protects data with built-in security, and supports both SQL and NoSQL workloads. - How does distributed SQL work?
Distributed SQL works as a single logical relational database deployed across a network servers, or nodes. It combines features of both SQL and NoSQL and automatically replicates and distributes data among the nodes. - When should you use distributed SQL databases vs. traditional relational databases?
Use distributed SQL databases when horizontal scalability, high availability, and multi-regional capabilities are needed. If these specific features aren’t required, a traditional relational database is a suitable option.