Connecting a Spring Boot Application to YugabyteDB Managed and Deploying It to Kubernetes on minikube
Spring Boot is one of the most popular frameworks for building cloud native applications. It makes configuring an application easy and offers tons of starters to get you off the ground quickly. Each Spring Boot application is stand-alone and self-contained, which makes them easy to deploy in a distributed fashion – to containers or, even better, on Kubernetes.
YugabyteDB Managed (formerly Yugabyte Cloud) is Yugabyte’s DB-as-a-service and is a perfect match for Spring Boot applications, especially ones made highly available with Kubernetes. YugabyteDB Managed gives you a PostgreSQL-compatible database that is resilient and scalable, just like the applications you run on k8s. You can scale your YugabyteDB cluster out (or in) with just a few clicks. So you can spend less time worrying about running your database and more time focused on building better software. It’s cloud native SQL for cloud native applications. Sign up for a free tier of YugabyteDB Managed today.
Walkthrough
In this post, we’ll walk you through connecting a Spring Boot application to YugabyteDB Managed and deploying it on minikube. You can explore our other walkthroughs on connecting a Spring Boot application to YugabyteDB Managed and deploying it on Kubernetes via Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) or via Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). We’ll be using a slightly updated version of the popular Spring Boot PetClinic sample application that has a profile making it compatible with YugabyteDB. The repository for this can be found at Github.
In this walkthrough, you will:
- Create a free YugabyteDB Managed account and database cluster
- Download the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application and connect it to YugabyteDB Managed
- Containerize the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application
- Start minikube
- Deploy the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application image to minikube
Prerequisites
Note: Anything in brackets [ ] needs to be replaced with information from your deployment.
Create a free YugabyteDB account and database cluster
1. Sign up for a YugabyteDB Managed account. After you’ve signed up and verified your email address, sign in.
2. Click the Create a Free Cluster button.
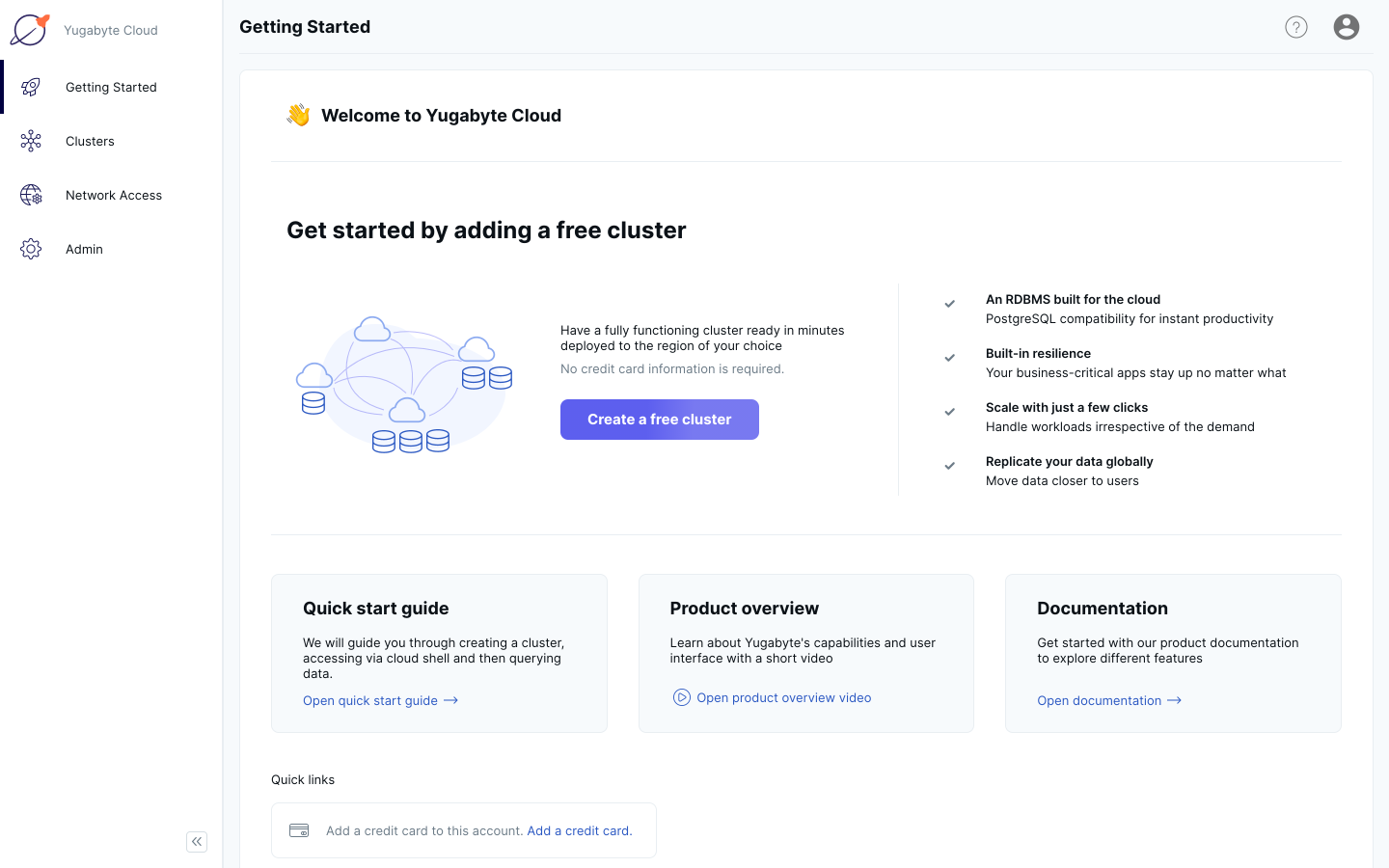
3. Select YugabyteDB Managed Free and click the Next button.
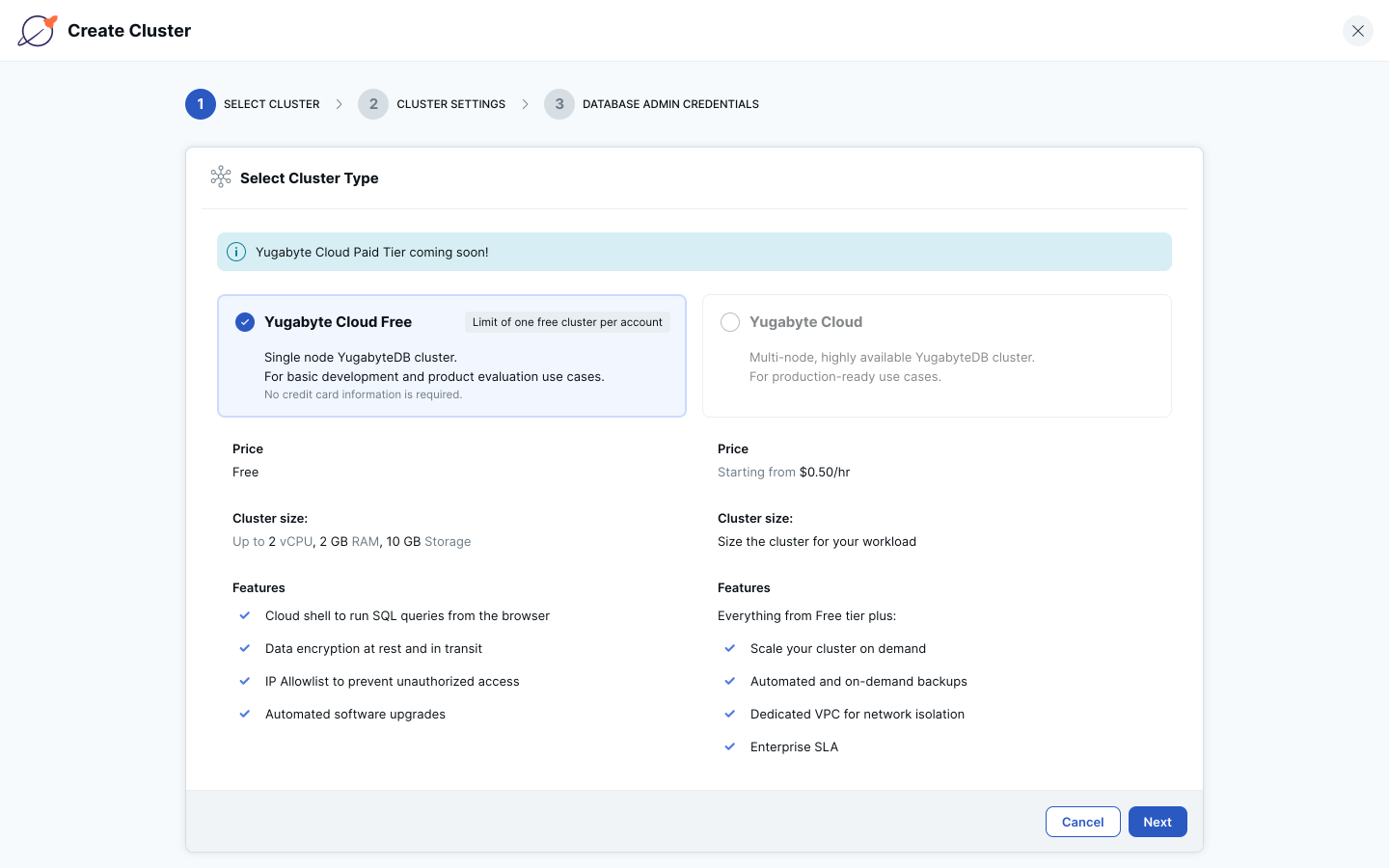
4. Select a cloud provider for your cluster, name your cluster, select a region, and click the Next button.
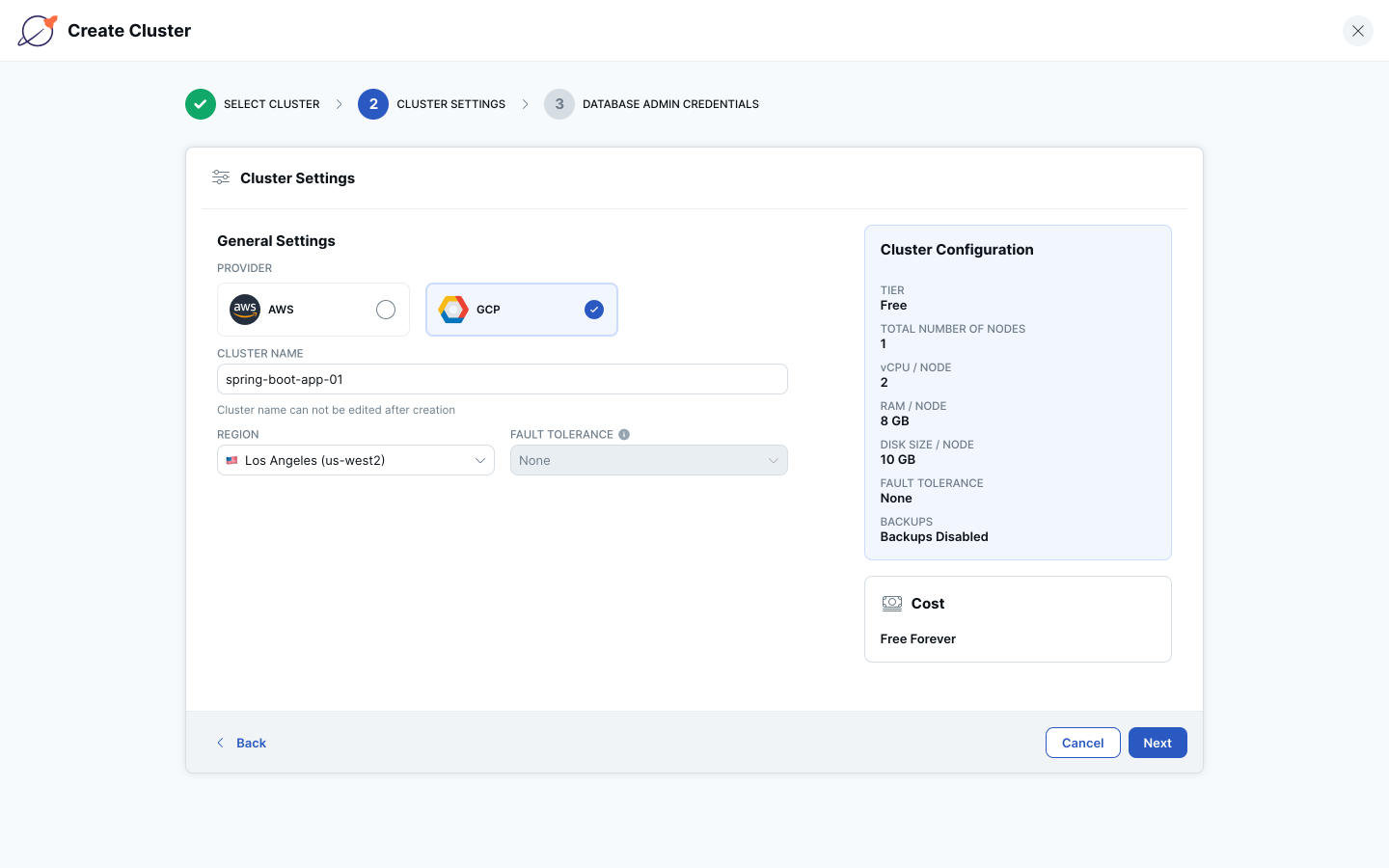
5. Copy the default admin credentials by clicking the Copy Credentials link. Then check the “I have copied the admin credentials” checkbox and click the Create Cluster button.
a. You can also set your own admin credentials by selecting the “Add your own credentials” radio button and entering your own credentials.
6. Wait for your cluster to be provisioned. Click on “Add IP Allow List” in the top section of the Clusters page.
7. Click the Create New List and Add to Cluster button.
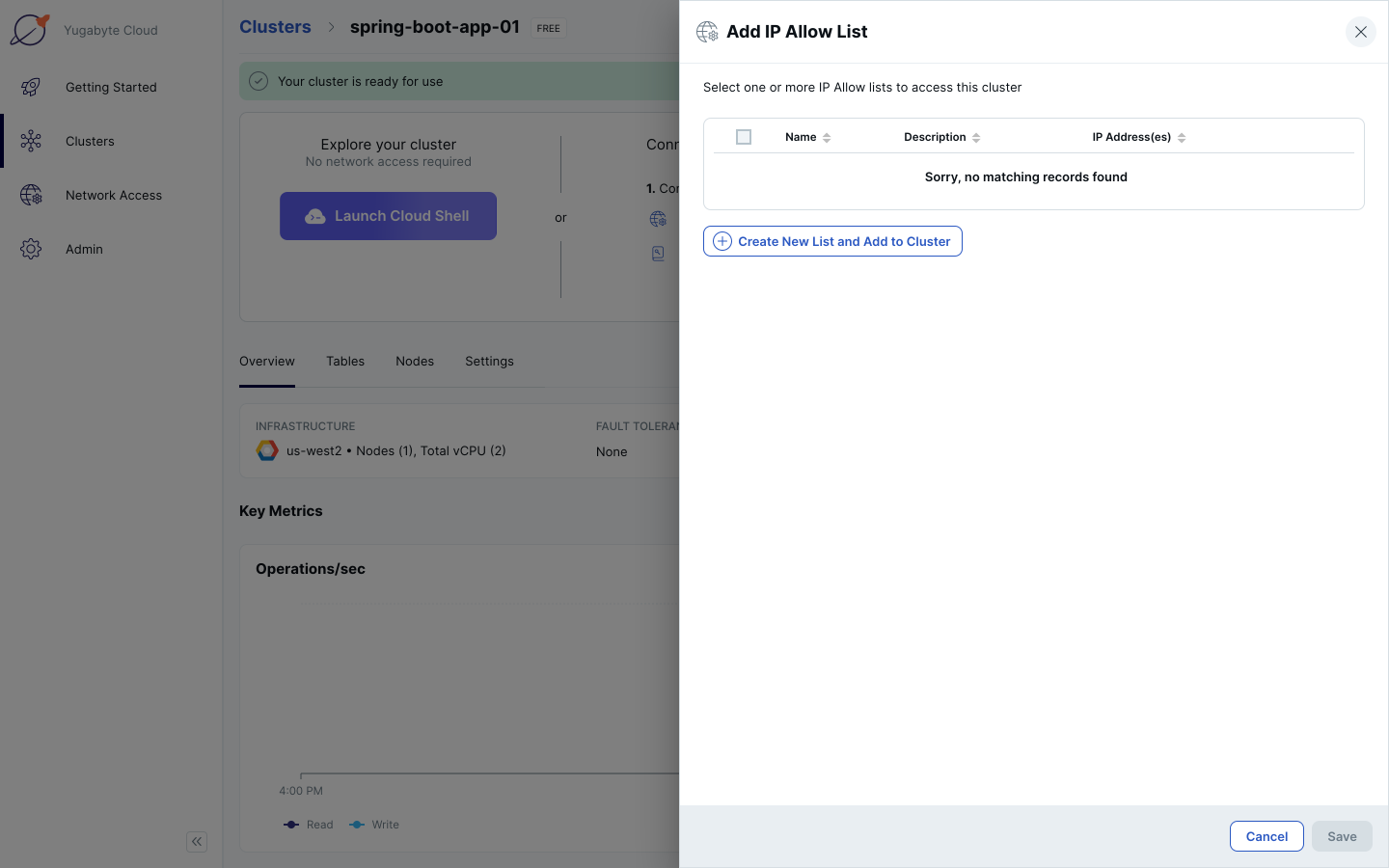
8. In the Name text box, enter “all-ips”. In the IP Address(es) or Range text box, enter “0.0.0.0/0”. Click the Save button. This will allow traffic from all IP addresses to your cluster.
a. Allowing all IPs access to your cluster is for development purposes only. When you deploy an application to Production, you will want to specify only the specific IP addresses or ranges that need access to your cluster.
Your cluster is now created in YugabyteDB Managed and is accessible to all IP addresses. Leave this page open, as you’ll be accessing the Cloud Shell later to create an application database and user.
Download the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application and connect it to your YugabyteDB account
Note: Instructions for how to connect this application to YugabyteDB are in spring-petclinic/src/main/resources/db/yugabytedb/petclinic_db_setup_yugabytedb.md from the repo you clone below.
1. On your computer from terminal, clone the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application: git clone https://github.com/yugabyte/spring-petclinic.git.
$ git clone https://github.com/yugabyte/spring-petclinic.git Cloning into 'spring-petclinic'... remote: Enumerating objects: 8616, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (18/18), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (18/18), done. remote: Total 8616 (delta 1), reused 13 (delta 0), pack-reused 8598 Receiving objects: 100% (8616/8616), 7.29 MiB | 19.03 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (3268/3268), done.
2. cd spring-petclinic.
3. Copy the contents of spring-petclinic/src/main/resources/db/yugabytedb/user.sql.
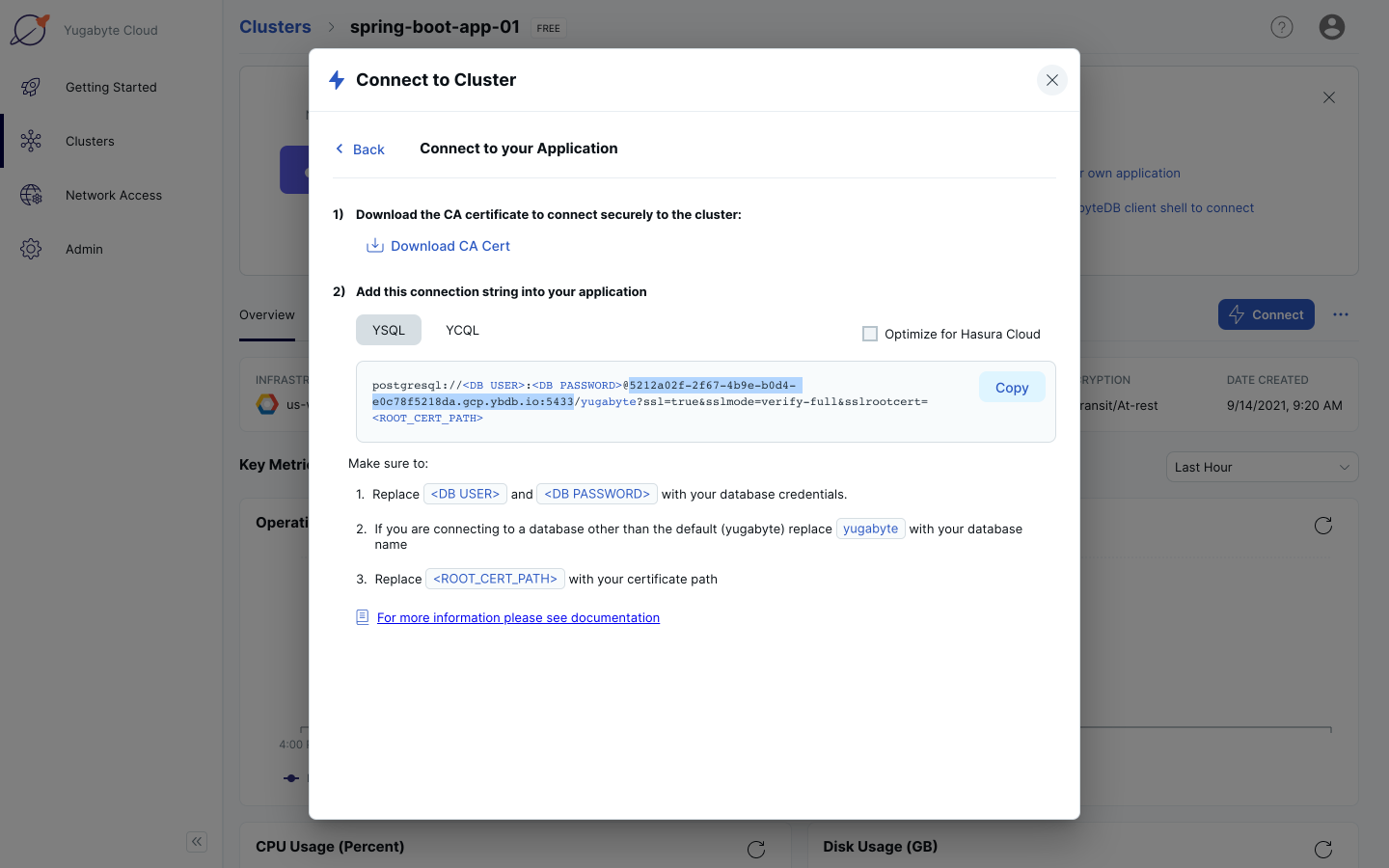
4. In YugabyteDB Managed, click on “Connect”. Click on Connect to your Application.
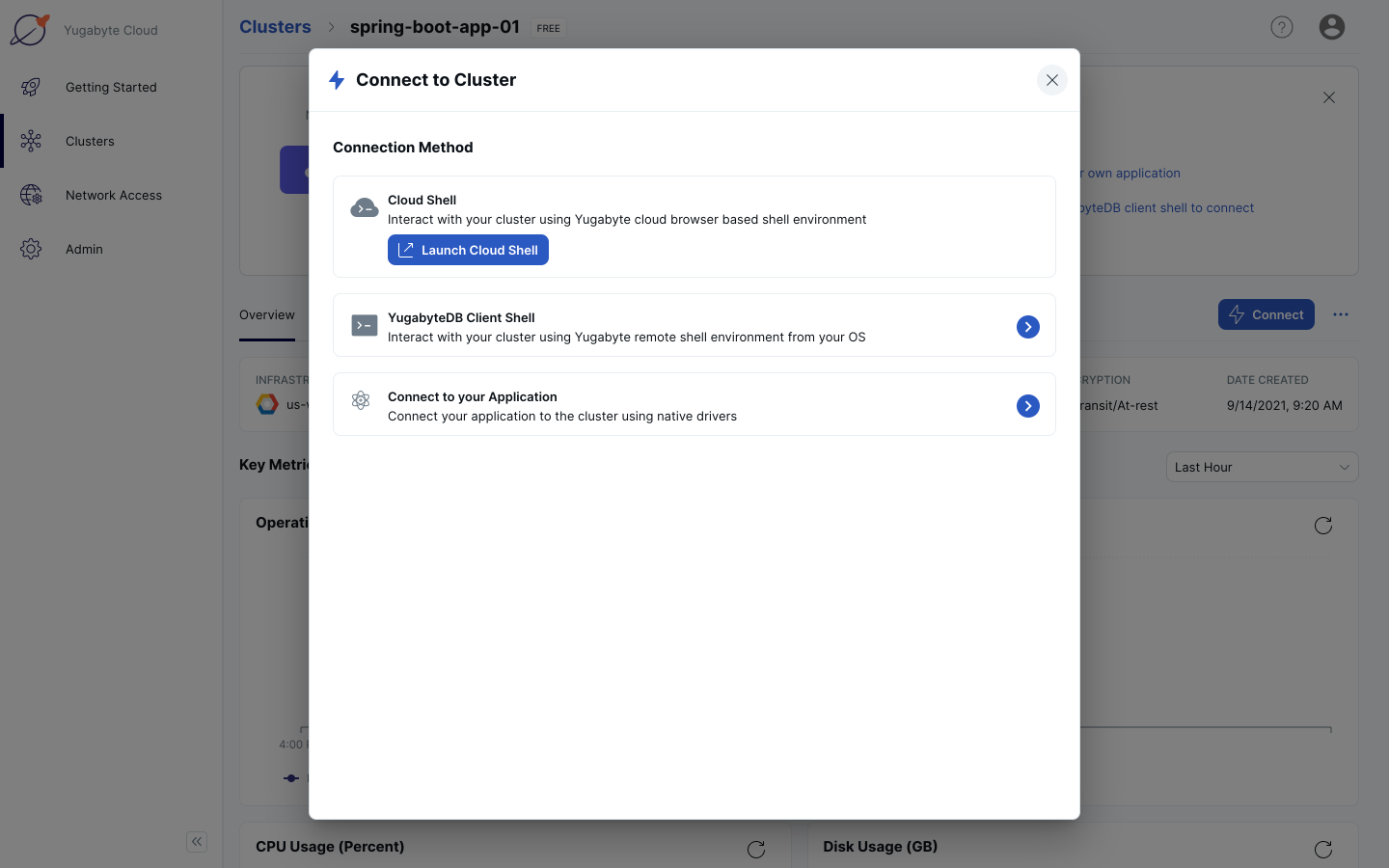
5. Save your host address and port (highlighted in the screenshot below) for later. Click the Back link in the Connect to Cluster navigation breadcrumb.
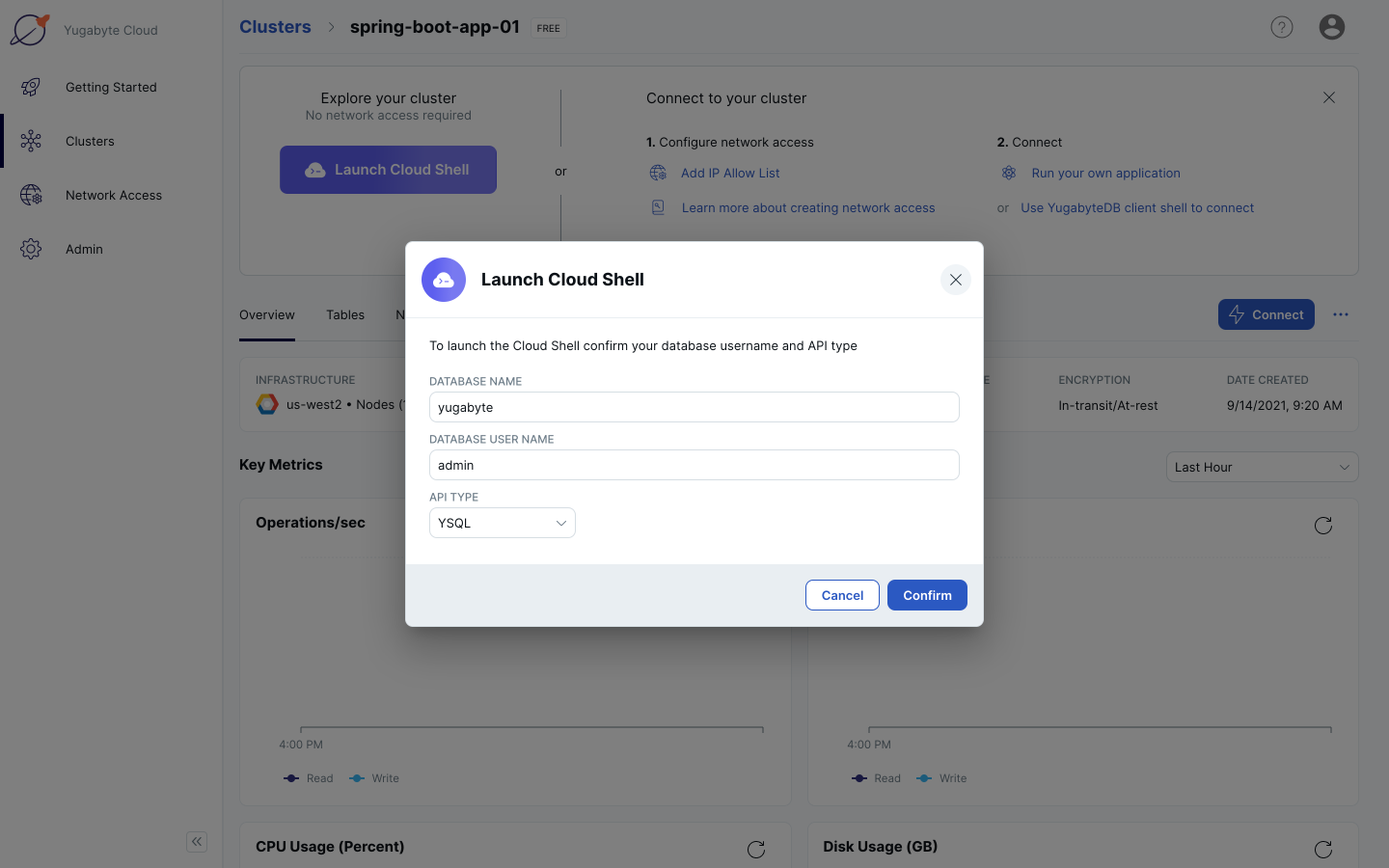
6. Click the Launch Cloud Shell button.
7. Leave the default Database Name, Database User Name, and API Type. Click the Confirm button. This will launch the Cloud Shell.
8. Enter the admin password you copied previously. After you enter the password, you will have a standard YSQL shell (exactly like a PSQL shell in PostgreSQL) that you can interact with from your browser.
Password for user admin: ysqlsh (11.2-YB-2.4.2.0-b0) SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.2, cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off) Type "help" for help. yugabyte=#
9. Go to https://localhost:8080. The PetClinic sample application should be available.
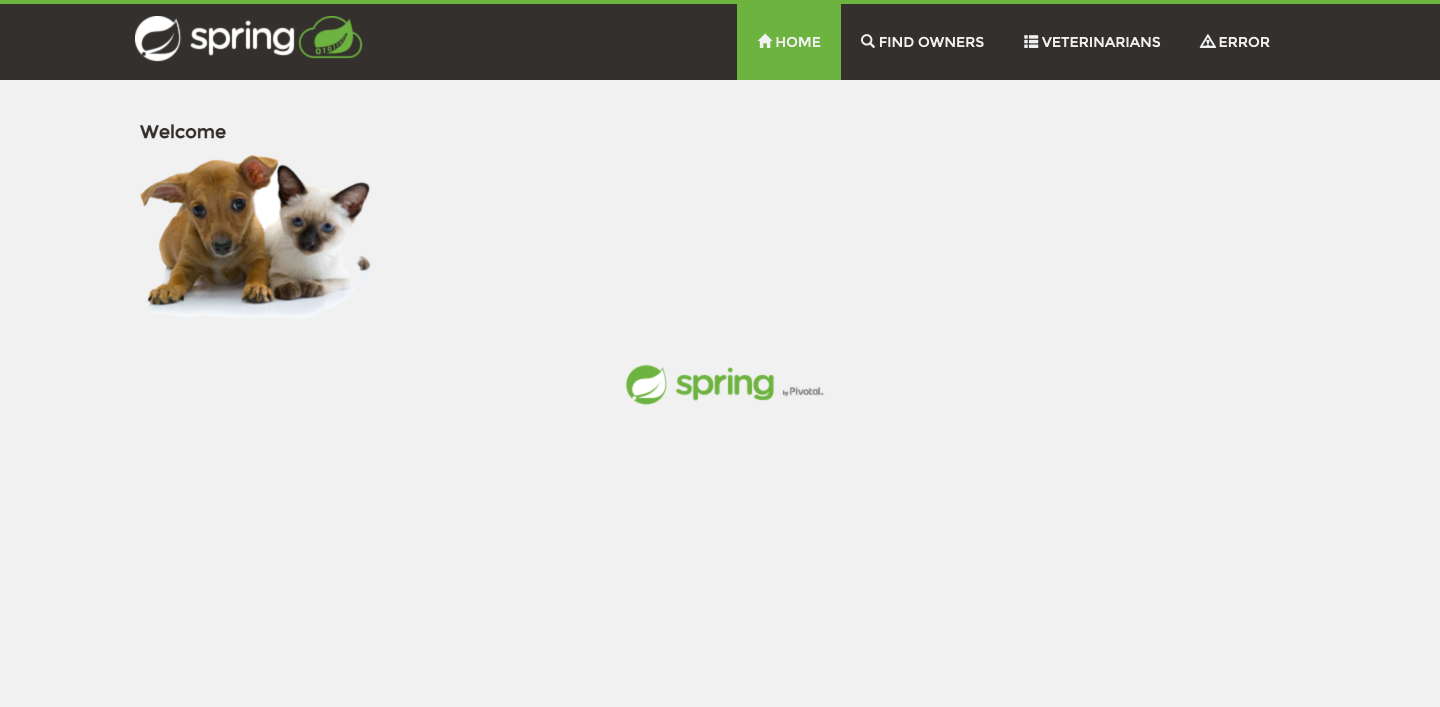
The PetClinic sample application is now connected to your YugabyteDB cluster and running locally.
Containerize the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application
1. Start Docker on your computer and containerize your Spring Boot PetClinic sample application: ./mvnw spring-boot:build-image.
2. Tag your image: docker tag [image_id] spring-petclinic – you can find your image id by running docker image ls.
3. Run your image as a container in Docker to make sure it’s working correctly: docker run -d --name=spring-petclinic -p 8080:8080 -e JAVA_OPTS="-Dspring.profiles.active=yugabytedb -Dspring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://[host]:[port]/petclinic?load-balance=true -Dspring.datasource.initialization-mode=never" spring-petclinic.
a. Go to https://localhost:8080. The PetClinic sample application should be available.
The PetClinic sample application is now connected to your YugabyteDB database cluster and running locally on Docker.
Start minikube
1. Start Docker (or another minkube-compatible container/VM manager) on your computer.
2. Open terminal and start minikube: minikube start
😄 minikube v1.22.0 on Darwin 11.5.1 (arm64) ✨ Automatically selected the docker driver 👍 Starting control plane node minikube in cluster minikube 🚜 Pulling base image ... 💾 Downloading Kubernetes v1.21.2 preload ... > gcr.io/k8s-minikube/kicbase...: 326.19 MiB / 326.19 MiB 100.00% 10.82 Mi > preloaded-images-k8s-v11-v1...: 522.45 MiB / 522.45 MiB 100.00% 15.90 Mi 🔥 Creating docker container (CPUs=2, Memory=4000MB) ... 🐳 Preparing Kubernetes v1.21.2 on Docker 20.10.7 ... ▪ Generating certificates and keys ... ▪ Booting up control plane ... ▪ Configuring RBAC rules ... 🔎 Verifying Kubernetes components... ▪ Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5 🌟 Enabled addons: storage-provisioner, default-storageclass 🏄 Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
3. Open a 2nd terminal and run: minikube dashboard
🔌 Enabling dashboard ... ▪ Using image kubernetesui/dashboard:v2.1.0 ▪ Using image kubernetesui/metrics-scraper:v1.0.4 🤔 Verifying dashboard health ... 🚀 Launching proxy ... 🤔 Verifying proxy health ... 🎉 Opening https://127.0.0.1:51726/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/ in your default browser...
That will open https://127.0.0.1:51726/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy. Keep this tab open. You’ll use it later to check on your application deployment.
Deploy the Spring Boot PetClinic sample application image to minikube
1. In your 1st terminal, point your shell to minikube’s Docker daemon — This will make it so that Docker and kubectl will use your minikube container registry instead of Docker’s container registry
Run: minikube docker-env.
export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY="1" export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://127.0.0.1:58018" export DOCKER_CERT_PATH="/Users/gavinjohnson/.minikube/certs" export MINIKUBE_ACTIVE_DOCKERD="minikube" # To point your shell to minikube's docker-daemon, run: # eval $(minikube -p minikube docker-env)
Run: eval $(minikube -p minikube docker-env) — last line in output above.
2. Build your image again: ./mvnw spring-boot:build-image.
3. Tag your image again: docker tag [image_id] spring-petclinic – you can find your image id by running docker image ls.
4. Create a new file named manifest-minikube.yml, enter the following contents, and save:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: spring-petclinic labels: run: spring-petclinic spec: selector: app: spring-petclinic ports: - protocol: TCP port: 8080 targetPort: 8080 type: LoadBalancer --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: spring-petclinic labels: app: spring-petclinic spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: spring-petclinic template: metadata: labels: app: spring-petclinic spec: containers: - name: spring-petclinic image: spring-petclinic imagePullPolicy: Never ports: - containerPort: 8080 env: - name: JAVA_OPTS value: "-Dspring.profiles.active=yugabytedb -Dspring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://[host]:[port]/petclinic?load-balance=true -Dspring.datasource.initialization-mode=never"
5. Create the Service and Deployment in minikube: kubectl create -f manifest-minikube.yml.
$ kubectl create -f manifest-minikube.yml service/spring-petclinic created deployment.apps/spring-petclinic created
6. Open a 3rd terminal and externally expose your load balancer: minikube tunnel
$ minikube tunnel 🏃 Starting tunnel for service spring-petclinic.
7. Wait for your application to come online (3 minutes or more for me).
8. If you go to the local IP and Port you configured in your yaml (https://127.0.0.1:8080), the PetClinic sample application should be available.

The PetClinic sample application is now connected to your YugabyteDB database cluster and running on Kubernetes locally on minikube.
Note:
If all else fails:
kubectl delete -f manifest-minikube.ymlminikube stopminikube delete --all
What’s Next?
Got questions? Feel free to ask them in our YugabyteDB community Slack channel.


